Code coverage in SonarCloud and GitHub Actions
How to obtain code coverage for a C# .NET Core 5 project in GitHub with actions
First of all I want to thank my friend Giulio Vian for pointing me in the right direction and for its great work in TfsAggregator Action.
My problem was: I used the wizard in GitHub to create a GitHub Action definition to analyze code in SonarCloud, everything runs just fine except I was not able to have Code Coverage nor unit tests result in my analysis. With Azure DevOps actions and .NET Full Framework project there is no problem but with GH and standard Actions no result see, seems to be uploaded.
Clearly this is not a problem of GH Actions, but it is due to a change in Sonar Cloud analysis tool, it happened in the past (when I had to manually convert code coverage output format for .NET core) and it seems that it happened again.
Running dotnet test command with standard code coverage collection options generates a result that is not usable by Sonar Cloud scanner.
After some tentative, I’ve decided to switch to a better approach, instead of changing GH Action Workflow, commit, then verify if the action is ok, I wrote a PowerShell script that does everything. This is one of my preferred approach, I can write the script, test it in Visual Studio Code or PowerShell ISE and, once the script runs correctly, I can simply call the very same script from GitHub action.
Using script usually cuts down time needed to develop CI/CD at least in half.
You can find complete code in this public GH repo. As first step I’ve included a .NET core tool configuration file in .config/dotnet-tool.json directory, with the following content:
| |
This file allows me to fix the exact version of all .NET core related tool that I need to use in this repository. As you can see I’ve included both GitVersion and dotnet-sonarscanner.
Even if you are not using dotnet, you should be aware that dotnet tools have lots of general purpose tools, like gitversion.
Once I’ve configured my tool list I can create a PowerShell file that does everything: restore tools, run gitversion, initialize code scanner, build test and complete code scanner. Many thanks to Giulio Vian that pointed me in the right direction about a couple of problems:
- You need to have a ProjectGuid in all .csproj of your project. This is not a requirement for .NET core so it is usually not present in csproj project files created by Visual Studio. You can add it manually or you can do this with PowerShell inside the script. Since I’ve not any problem in having it inside my .csproj file, I’ve directly modified my projects files to include a ProjectGuid.
- You need to execute dotnet test with special parameters to have output in a format that is understandable by SonarCloud.
Performing the whole set of steps in a PowerShell file speeds up problem solving because you can directly launch the script in your machine, debug it, and verify if everything works as expected.
This is the complete script that analyze my project. It has sonarSecret as the only parameter, it does not need anything else. You can use this PowerShell file to launch an analysis in your Machine without committing anything. It is not a good practice to analyze uncommitted code, but it is really good for troubleshooting.
Here is the complete content of the file.
| |
Once the script works correctly, you can simply invoke it in a run task in your GH Action (or in an Azure Devops pipeline, or in any CI tool you are using). Resulting action script is really simple, very few lines of code.
| |
The only special step I’m using is the standard actions/setup-java@v1 that automatically setup java to be used in subsequent steps of the action. As you can verify I can simply call sonarcloud.ps1 script and let the script doing everything". After a run is complete I can verify if finally code coverage appears in SonarCloud dashboard.
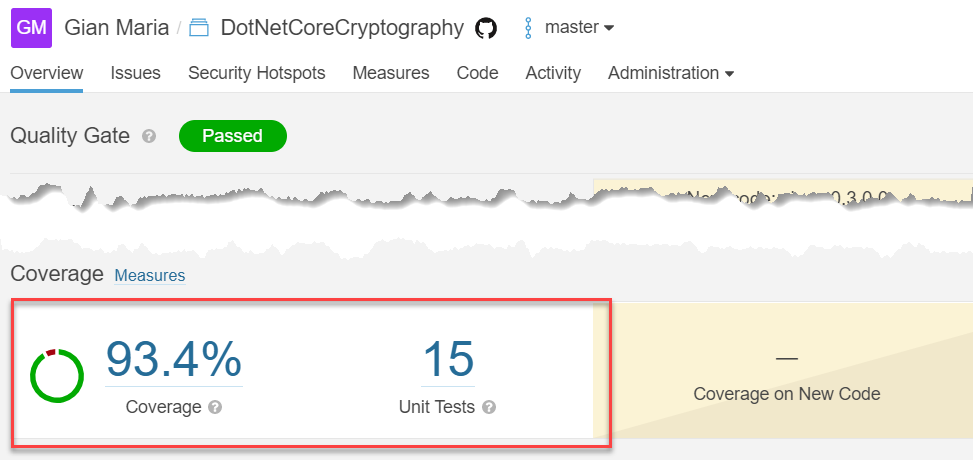 Figure 1: Result of Sonar Cloud analysis now includes code coverage
Figure 1: Result of Sonar Cloud analysis now includes code coverage
If you want to really be sure that code coverage is running inside the action, just check the log to find importing log for code coverage as shown in Figure 2.
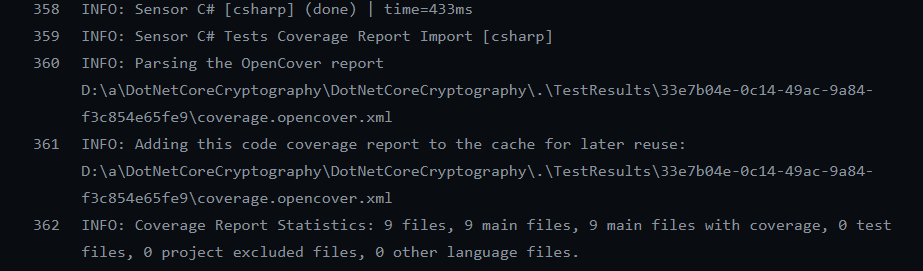 Figure 2: Output of scanner analyzer shows that code coverage result was found and analyzed
Figure 2: Output of scanner analyzer shows that code coverage result was found and analyzed
The nice aspect of this approach is the ability to test everything locally with the help of PowerShell IDE (ISE, VSCode), you can simply modify/debug your script until it does what you want and once it is done, simply invoke it from the action and commit everything.
Gian Maria.
